A Dynamic and Interconnected System
Earth is not a static sphere; it’s a dynamic and interconnected system where various components interact and influence each other in complex ways. Understanding these intricate relationships is crucial for comprehending the past, present, and future of our planet.
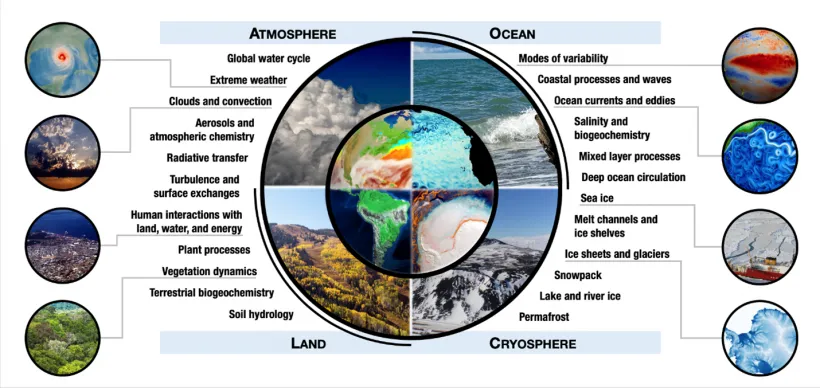
Key Earth Systems:
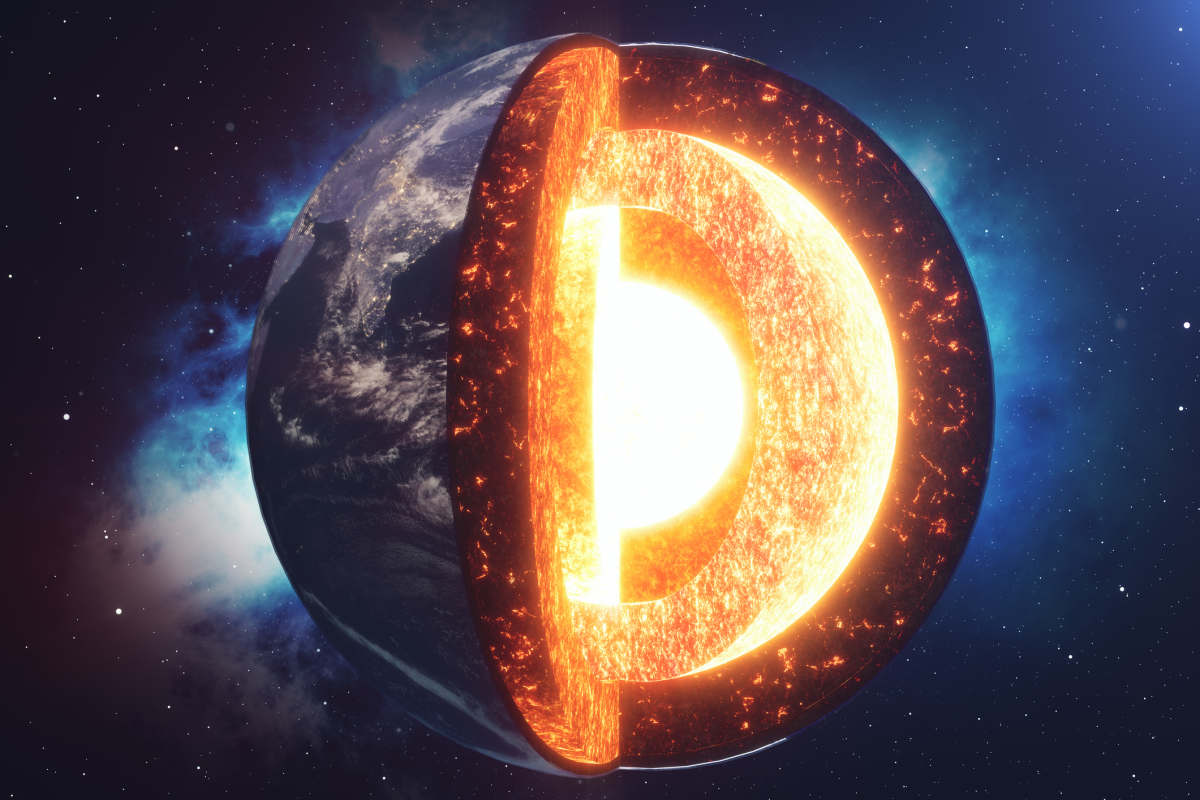
- Geosphere: The solid, non-living parts of Earth, including the crust, mantle, and core. Key processes within the geosphere include plate tectonics, which drives the movement of continents and the formation of mountains and volcanoes.
- Hydrosphere: The water component of Earth, encompassing oceans, rivers, lakes, groundwater, and ice. The hydrosphere plays a vital role in regulating Earth’s climate, transporting nutrients, and shaping landscapes.
- Atmosphere: The gaseous layer that surrounds Earth, composed primarily of nitrogen and oxygen. The atmosphere protects life from harmful solar radiation, regulates temperature, and drives weather patterns.
- Biosphere: The living component of Earth, encompassing all living organisms and their interactions. The biosphere plays a crucial role in shaping the Earth’s environment, influencing the composition of the atmosphere, and driving biogeochemical cycles.
Interconnections Between Earth Systems:
These four spheres are intricately interconnected. For example:
- Plate tectonics can trigger volcanic eruptions, releasing gases into the atmosphere and influencing climate.
- Ocean currents transport heat around the globe, influencing weather patterns and climate.
- Living organisms play a crucial role in the cycling of carbon and other elements, impacting the atmosphere and climate.
- Climate change can alter the distribution of water, impacting ecosystems and human societies.
The Importance of Earth Science:
Understanding the science of our planet is essential for addressing global challenges such as climate change, natural disasters, and resource management. By studying Earth’s systems, scientists can:
- Predict and mitigate natural hazards: Such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and floods.
- Understand and address climate change: By studying climate patterns, identifying the drivers of climate change, and developing strategies for mitigation and adaptation.
- Manage natural resources: Such as water, soil, and minerals, in a sustainable manner.
- Protect biodiversity: By understanding the interconnectedness of ecosystems and the impacts of human activities on biodiversity.
Conclusion
Earth is a complex and dynamic planet, and its systems are interconnected in profound ways. By studying the science of our planet, we can gain a deeper understanding of the forces that shape our world and develop strategies for a sustainable future.
Disclaimer: This information is for general knowledge and informational purposes only and does not constitute professional advice.